Introduction: Why Logging and Monitoring Matter in AWS
Logging and monitoring are the starting points for any security incident response workflow in AWS. This was also mentioned in the AWS Security Incident Response Guide. Chiefly, they provide timely visibility to observe and know what is happening within the AWS environment. Having these centralized provides a unified view, consolidating activity from multiple accounts and services across AWS. Typically, monitoring and logs include API calls, metrics, and network traffic across the AWS environment, captured by CloudTrail, CloudWatch, and VPC Flow Logs. Another essential service in AWS Config is that it records configuration changes, which helps to identify unauthorized or unexpected modifications. Overall, continuous monitoring instantly uncovers anomalies, enabling more prompt awareness and action.
There are several other reasons why AWS logging and monitoring are the foundation for incident response. The detailed logs generated assist with forensic activities by providing the evidence needed to trace security incidents accurately. They also enable automated detection by integrating alerts from services like GuardDuty and Security Hub, helping to identify threats as they occur. They integrate with EventBridge and Lambda to isolate compromised resources immediately. Logs are vital for post-incident learning since their post-event analysis strengthens future detection and prevention strategies.
AWS logging and monitoring are also essential for security and compliance assurance by providing regulatory alignment. Continuous logging maintains auditable records and thereby supports frameworks like ISO 27001, SOC 2, and PCI DSS. It also tracks user and API actions, verifying that only authorized entities are performing sensitive operations. Furthermore, automated monitoring contributes to policy enforcement by ensuring security controls remain active and compliant across all AWS resources. Automated monitoring also provides operational efficiency by enabling proactive issue detection, reducing downtime, and improving performance.
Understanding AWS Logging and Monitoring

Defining Logging and Monitoring in AWS
It is essential to define logging and monitoring properly, especially within the context of the AWS environment. Logging activities capture detailed records of system and user activities across AWS resources for subsequent auditing and analysis. Meanwhile, monitoring observes key metrics including performance, availability, and security in real time. Combining these provides a continuous feedback loop, helping to detect anomalies, troubleshoot issues, and maintain security visibility.
The Shared Responsibility Model
Amazon established the shared responsibility model between itself and its customers for protecting their resources running on AWS. AWS is responsible for securing the cloud infrastructure that includes hardware, networking, and managed service foundations. Meanwhile, customers must secure their own AWS workload in the cloud by configuring logging, monitoring, and access controls for their own resources. This enables effective security by collaboration with both Amazon and its customers, fulfilling their roles to maintain complete visibility and compliance.
Core Logging Services Overview
Several AWS core services provide end-to-end logging of system and user actions across AWS accounts. Firstly, AWS CloudTrail records all API calls and user activities, resulting in a complete audit trail across accounts and services. Another service is VPC Flow Logs, which captures network traffic information to help identify unusual communication patterns or potential intrusions. The other core service is AWS Config, which tracks configuration changes over time. This enables compliance checks and detection of unauthorized modifications.
Monitoring and Metrics Services
AWS also provides core monitoring services besides logging. The primary service is Amazon CloudWatch, which collects and visualizes metrics from AWS resources and applications in real time. Supporting this are CloudWatch Alarms that trigger automated actions or notifications whenever metrics breach established thresholds. The other supporting services are CloudWatch Dashboards that centralize key performance indicators, enabling quick assessment of system health and trends.
Threat Detection and Analysis Tools
AWS logging and monitoring services are the first stage in the security workflow; it is essential to consider the subsequent stages that process and act on logs and alerts. The Amazon GuardDuty service continuously analyzes logs to detect malicious activity, unusual behavior, and potential threats. Since there are hundreds of accounts, AWS Security Hub performs aggregation and prioritizes findings from multiple security services into a single dashboard. For further investigation, Amazon Detective provides a more detailed analysis by visualizing relationships among resources, events, and threat patterns.
Integration Across Services
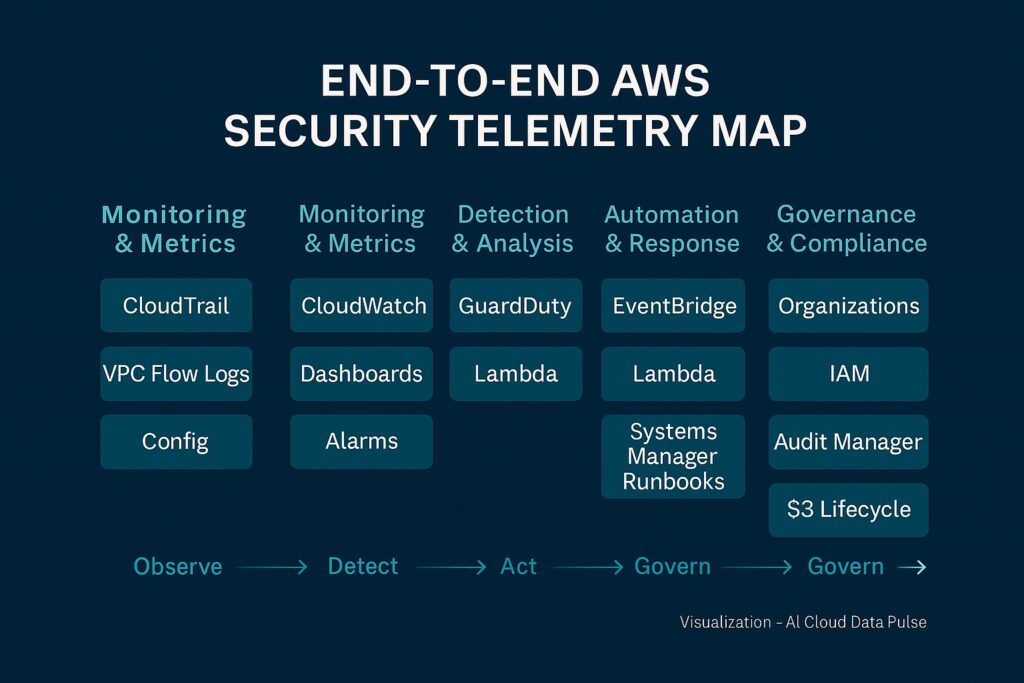
AWS provides a rich array of services for logging, monitoring, threat detection, and analysis. It also enables the seamless integration of these services to ensure consistent visibility and detection across all AWS layers. Therefore, there is seamless data flow between CloudTrail, CloudWatch, and GuardDuty to process logs and metrics. Responding to logs or alerts indicating security events is handled by EventBridge and Lambda, automating incident response workflows. Finally, it is critical to unify alerts and compliance checks using Security Hub to provide a centralized view of the security posture.
Multi-Account and Organization-Level Visibility
AWS Organizations and AWS Control Tower complement Security Hub for centralized management of security events. Firstly, AWS Organizations allows security teams to centrally manage accounts and ensure consistent logging and monitoring policies across the environment. Next, AWS Control Tower handles automated account setup, along with built-in logging baselines that route all logs to a central S3 bucket. Finally, security teams use cross-account access, which allows them to analyze logs and metrics from multiple accounts without compromising isolation.
Designing a Centralized Logging Architecture
Once security engineers have an understanding of AWS logging and monitoring, they can design and build a centralized logging architecture.
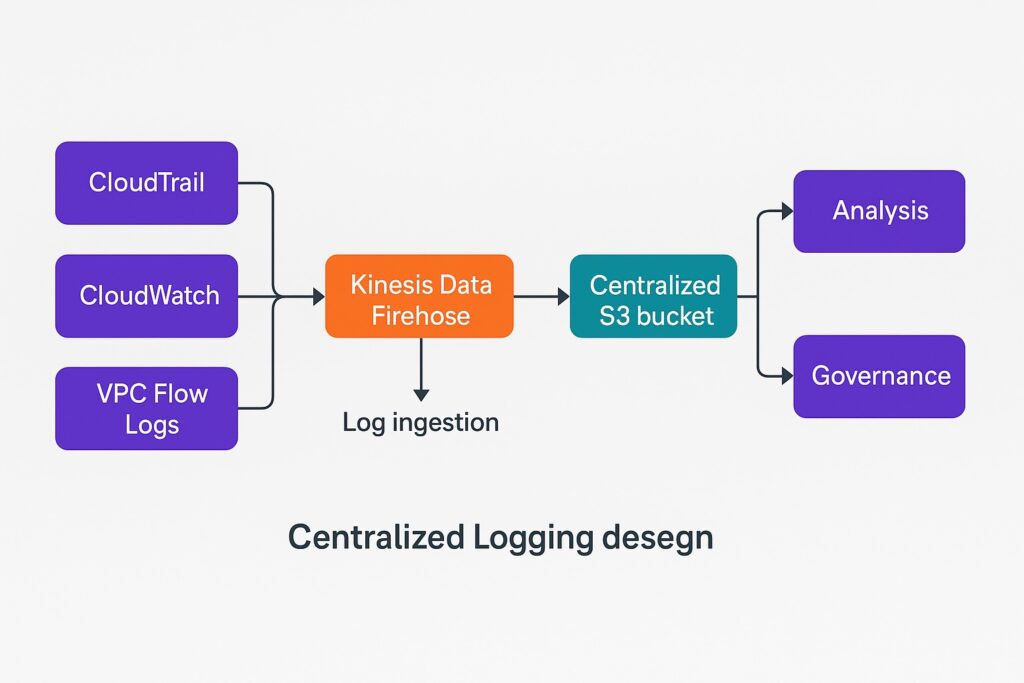
Centralized Logging and Monitoring Collection
When centralizing logging, the logging architecture should store all logs in a single place. Therefore, it should aggregate all logs from all AWS accounts and regions into a single, centrally managed S3 bucket. Furthermore, security engineers should set up AWS Organizations or Control Tower to enforce standardized logging configuration across all accounts. Additionally, they should configure CloudTrail, CloudWatch, and VPC Flow Logs to automatically route logs to the centralized bucket. The unified log repository improves visibility by simplifying analysis, correlation, and long-term retention management.
S3 Bucket Configuration and Security
Security engineers should set up dedicated log buckets for logging, ensuring they are not accidentally modified or deleted. Additionally, they need to ensure data protection by enabling server-side encryption with AWS KMS for encryption at rest. They also need to enforce HTTPS for all data transfers for encryption in transit. Finally, they must apply least-privilege IAM policies and block public access to ensure only authorized services can write to the bucket.
Log Ingestion and Delivery
Next, security engineers need to establish data transfer from the AWS logging and monitoring services to the S3 buckets. They can use Kinesis Data Firehose, which automatically delivers log data from CloudTrail, CloudWatch, and VPC Flow Logs to S3. Storage formats in S3 are also critical for cost and efficient access. Therefore, security engineers should configure Firehose to compress and convert logs into Parquet or JSON. Finally, engineers must guarantee a reliable transfer from logging services to S3. Hence, they should enable error logging and retry mechanisms to ensure logs are consistently delivered without data loss.
Cross-Account Access Management
Logs originate from accounts other than the storage account. Therefore, security engineers should use IAM roles to allow these source accounts to securely write logs to the central S3 bucket. They should build defense in depth by applying S3 bucket policies that grant write-only permissions to prevent log tampering or deletion. Finally, they should make the logging buckets visible to only designated security or audit accounts to maintain data isolation and integrity.
Encryption and Key Management
To implement encryption at rest, security engineers should use AWS KMS-managed keys with server-side encryption (SSE-KMS). Furthermore, to maintain strong cryptographic hygiene according to best practices, they should enable automatic or scheduled key rotation. They should also limit key usage and administration rights to authorized security and compliance personnel only.
Data Normalization and Indexing
The logs come from diverse sources, and normalizing them will allow their integration in a central location. Security engineers can use AWS Glue to catalog and normalize log data into a consistent schema. Also, another advantage of partitioning and compressing data sets is that security teams can use Amazon Athena to analyze logs directly in S3. To enable fast searches and visual dashboards, security teams should index these normalized logs in Amazon OpenSearch.
Monitoring and Alerting for the Log Pipeline
Security teams should also establish monitoring for the logging pipeline to maintain its health and effectiveness. Therefore, CloudWatch metrics should track delivery success rates, latency, and ingestion errors. Next, security teams should configure CloudWatch Alarms to notify or trigger remediation workflows to respond to anomalies whenever they arise. Finally, security teams should ensure full traceability and compliance verification by logging all pipeline events and access attempts.
Benefits of Centralized Logging
In summary, centralized logging improves visibility with a single log repository providing a complete view of activities across all AWS accounts and regions. This simplifies compliance, where centralized storage streamlines auditing and ensures consistent enforcement of retention policies. This also leads to faster incident response because unified access to logs accelerates detection, investigation, and remediation of security events.
Monitoring for Security and Performance Alongside Logging
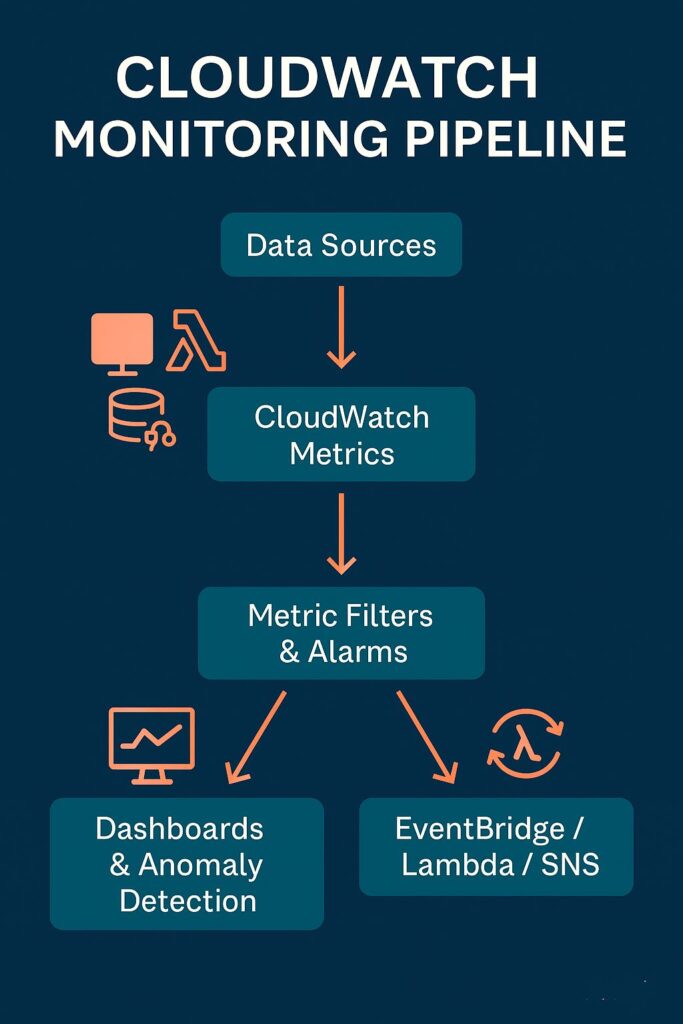
CloudWatch Metrics and Dashboards
In addition to logging, metrics allow real-time monitoring of AWS resources’ health, and CloudWatch collects these metrics and tracks key performance metrics in real time. Additionally, it is essential to visualize these metrics, and CloudWatch Dashboards provide a unified view of system health and utilization. Additionally, security teams can set up custom metrics for application-specific monitoring.
Metric Filters for Security Events
Whenever these metrics, individually or collectively, exhibit specific values, they can indicate various security events. Hence, applying filters on these metrics can allow detection of specific log patterns such as failed logins or access denials. Additionally, they enable monitoring configuration changes in IAM roles and security groups. Security teams can use the outputs of these filters to trigger alerts for unauthorized API calls or root account activity.
Alarm Configuration and Notifications
Alarms are the subsequent stage for metrics and metric filters, allowing automated or manual responses to security events. Security teams define CloudWatch Alarms for critical metrics that trigger whenever their values cross predefined thresholds. These alarms send real-time notifications to security personnel via email or SMS using Amazon SNS. Additionally, alarms can initiate automated remediation workflows by triggering AWS Lambda functions.
Anomaly Detection and Predictive Insights
Many security issues manifest themselves through deviations from normal metric patterns. Therefore, identifying these deviations can uncover the presence of security events. Security personnel can use CloudWatch Anomaly Detection to identify these anomalies and, in turn, their underlying security issues. This service can also predict potential performance or security issues by applying machine learning models. Subsequently, it can generate early warnings that help teams investigate and respond before incidents escalate.
EventBridge for Automation of Logging and Monitoring
EventBridge is the critical component for translating metric alerts into automated, actionable responses. It captures events from AWS services, applications, and custom sources in real time. Subsequently, it applies rules to these events to trigger automated security or operational workflows. Additionally, it integrates with Lambda, Step Functions, and Amazon SNS for a scalable response to security events.
Visualization and Correlation Tools
While automated responses are core to handling security events, human oversight is still required. Amazon OpenSearch Dashboards provides this capability by allowing security teams to visualize and interactively explore log data. Also, it enables correlation of security and performance metrics across multiple AWS services. Whenever security personnel need advanced analytics and executive-level reporting, they can use Amazon QuickSight.
Continuous Improvement through Monitoring Reviews
No matter how good, all systems need continuous improvement. They also need to adapt to the changing threat landscape. Therefore, security teams should continually improve their practices and processes. They should conduct regular reviews of dashboards, alarms, and anomaly detection results. Additionally, they should adjust thresholds and alert rules based on evolving workloads and trends. Furthermore, security personnel must incorporate lessons learned from incidents to refine monitoring strategies.
Benefits of Proactive Logging and Monitoring
Proactive monitoring of system metrics enhances reliability by detecting and addressing issues early. Subsequently, it reduces mean time to detect (MTTD) and mean time to respond (MTTR). Furthermore, proactive monitoring supports continuous compliance through ongoing visibility and validation.
Detecting and Investigating Threats From Logging and Monitoring
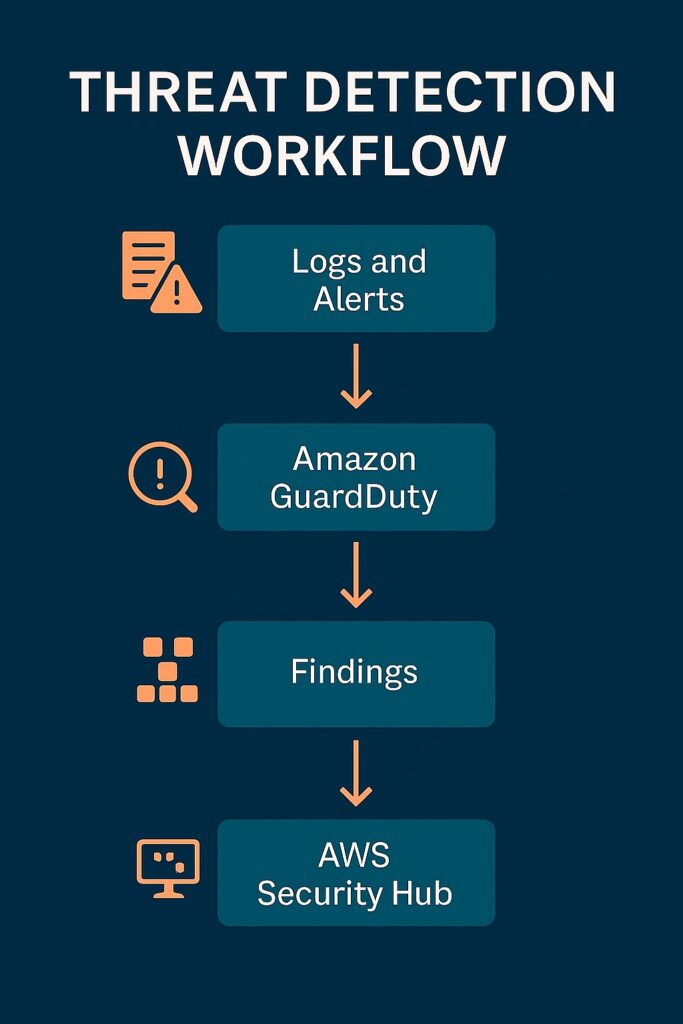
Importance of Threat Detection in AWS
AWS logging and monitoring make up the first stages of the security incident handling pipeline. However, subsequent stages are just as critical, including detecting and investigating threats. This capability allows security personnel to identify malicious activities early before they impact system integrity or availability. It also enables them to have continuous visibility across AWS accounts, workloads, and network traffic. Therefore, they can strengthen compliance by ensuring the timely detection and reporting of security incidents.
AWS GuardDuty Overview
AWS GuardDuty supports threat detection by continuously analyzing logs from AWS CloudTrail, VPC Flow Logs, and Route 53 Resolver DNS query logs for suspicious or unauthorized activity. It uses threat intelligence feeds and machine learning to detect anomalies and potential security threats. From these outputs, it then generates detailed findings that highlight affected resources and recommended remediation actions.
Security Hub as the Central Aggregator
AWS services supporting threat detection each provide different aspects of the threat landscape. Aggregating their outputs provides a more complete picture of the threat environment to security personnel. Therefore, Security Hub aggregates findings from these services, such as GuardDuty, Inspector, and Macie. Another important activity that it does is normalizing and prioritizing these security alerts for centralized visibility. Also, it integrates with third-party tools and SIEM platforms to enrich visibility for unified threat management.
Amazon Detective for Investigation
Threat detection is critical, yet it remains insufficient. Therefore, security personnel must investigate these threats and utilize powerful tools due to their sophisticated nature. Such a tool is Amazon Detective, which visualizes relationships among AWS resources, users, and events to trace security incidents. It also analyzes data from CloudTrail, VPC Flow Logs, and GuardDuty findings for root cause analysis. The other key benefit is that it provides interactive graphs and contextual evidence exploration to simplify investigation workflows.
Integration with AWS Config
Amazon Detective also correlates its security investigations with AWS Config since suspicious changes in system configuration can point to malicious activity. It achieves this by reviewing the historical resource states and matching them with current states to detect unauthorized changes. Therefore, it can provide deep contextual insight by linking user actions, resource histories, and detected threats.
Automated Response and Remediation
Once personnel have detected a threat, they must neutralize it and perform any necessary remedial actions. They can configure AWS EventBridge rules to automatically respond to GuardDuty or Security Hub findings. Subsequently, they trigger AWS Lambda functions, which neutralize threats by isolating them or remediating compromised resources. AWS EventBridge can also trigger Lambda functions via Systems Manager Automation runbooks to ensure consistency with incident response actions. For a detailed walkthrough of building automated response pipelines using these services, refer to our related article, Automated Incident Response in AWS.
Collaboration and Incident Workflows
Logging and tracking security incidents is as essential as their remediation, and teams should log these in collaboration tools like Jira and Slack. Furthermore, they should integrate these with SIEM platforms to centralize incident tracking and correlation. Security teams must collaborate with operations and compliance teams, and using these tools will enable coordinated response workflows.
Retention, Compliance, and Cost Optimization for AWS Logging and Monitoring Artifacts
Best practices recommend applying lifecycle management to artifacts generated by AWS Logging and Monitoring.
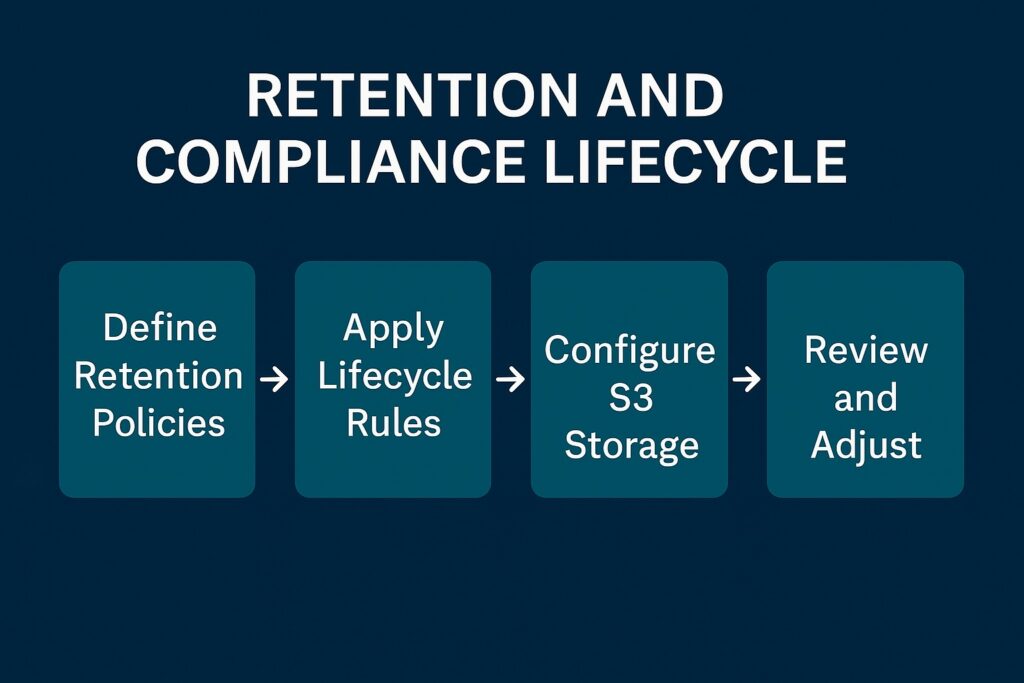
Monitoring and Logging Retention Policies
It is necessary to retain logs due to organizational, legal, and compliance requirements, and they have differing retention periods. Therefore, security governance should define, differentiate, and document retention periods between audit, security, and organizational logs. Subsequently, security teams should document and enforce these retention policies through AWS Organizations and AWS Config rules.
Storage Tiering and Lifecycle Management
After defining retention periods, cloud administrators must then specify the most secure and efficient way for log retention. S3 provides a rich set of storage tiers, including S3 Standard, S3 Glacier, and S3 Glacier Deep Archive. It also makes available lifecycle policies for transitioning data between these tiers. Administrative teams can then define lifecycle policies for log data transitions between storage tiers. Furthermore, they can set data transition automation through S3 lifecycle rules that optimize storage costs while maintaining accessibility. They also need to periodically review and adjust these tiering schedules based on retention requirements and the frequency of data access.
Regulatory Compliance and Audit Readiness
A core need for AWS logging and monitoring artifacts retention is compliance frameworks, such as ISO 27001, SOC 2, and PCI DSS. AWS administrators should configure AWS logging and monitoring to these compliance frameworks. They must maintain auditable records through continuous logging and immutable storage for regulatory verification. S3 object lock capabilities are available to achieve this. AWS Config and Audit Manager services are available for administrators to automate evidence collection and compliance reporting.
Access Control and Data Integrity for AWS Logging and Monitoring
Given the criticality of logs for legal and regulatory compliance, it is paramount to guarantee their integrity. Access control is also vital, and administrators must enforce least-privilege access using AWS IAM roles and policies for logging data and monitoring resources. Also, to protect data integrity and confidentiality, they must implement S3 bucket policies and AWS KMS encryption. Similar to logging for security events, administrators should also enable CloudTrail log file validation to detect any unauthorized modifications to log files.
Encryption and Secure Archival
Administrators should also extend data integrity protection by encrypting log data at rest across all S3 storage tiers using AWS KMS-managed keys (SSE-KMS). Log data is also transferred between different AWS services and S3, where administrators must enforce TLS encryption for data in transit. Additionally, they should apply access restrictions and encryption for log data archived in S3 Glacier or Deep Archive with Vault Lock to prevent deletion during their retention period.
AWS Cost Analysis and Optimization Strategies for Logging and Monitoring
AWS Cloud governance must ensure good cost management of logging and monitoring. Administrators can use AWS Cost Explorer and AWS Budgets to identify optimization opportunities when analyzing storage costs across S3 tiers. Additional processes include implementing data compression, partitioning, and lifecycle transitions to reduce storage and query costs. They should also use S3 Storage Lens and AWS Cost Explorer services for visibility into usage patterns and cost-saving recommendations.
Automated Lifecycle and Deletion Processes
Log data governance involves transitioning data between S3 storage tiers and expirations based on retention duration. Therefore, it should automate these activities based on their retention policies. They should use S3 Object Expiration to automate data expiry and Intelligent-Tiering to reduce manual intervention. Furthermore, governance should regularly review and audit lifecycle policies to ensure deletion schedules align with compliance and governance requirements.
AWS Logging and Monitoring Access Control and Governance
Regulatory and legal compliance place onerous demands upon AWS Logging and Monitoring. Therefore, it is paramount to have access control and governance on logs and metrics.

Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Least Privilege
Governance and AWS administrators should define IAM roles for logging, monitoring, and analysis separately for fine-grained access control. These should reflect least-privilege policies that they should apply to CloudTrail, CloudWatch, and S3 access. Also, when integrating with services such as GuardDuty, Security Hub, and Detective, they should use service-linked roles.
Policy Enforcement Using AWS Organizations
AWS administrators should also centralize control using Service Control Policies (SCPs) to restrict unauthorized changes. Additionally, they should look to apply preventative guardrails for disabling CloudTrail either accidentally or deliberately, and prevent S3 log bucket deletion. The other architectural best practice is delegating the administration of security services to the organization’s management account.
Secure Delegation and Cross-Account Permissions
To further secure AWS logging and monitoring, use IAM roles with defined trust policies for cross-account access. Alongside this, security teams should restrict role assumption only to designated security or audit accounts. Security governance should regularly audit role sessions and access patterns through CloudTrail insights.
Monitoring Access Activities and Anomalies
Furthermore, administrators should police the policeman by enabling CloudTrail data events for IAM, S3, and KMS activities. Additionally, they should also set CloudWatch alarms for policy changes, denied actions, or excessive role assumptions. They should also feed these access logs into Security Hub to provide centralized visibility and correlation.
Governance Reviews and Continuous Improvement
Any governance must have ongoing introspection and look for opportunities for improvement; this is especially the case with cybersecurity. Therefore, security governance and security teams must conduct periodic reviews of IAM policies and role assignments to ensure adherence to best practices. Furthermore, they should validate alignment with compliance and organizational policy baselines. Additionally, security teams should use services like AWS Access Analyzer and IAM Policy Simulator to identify and remediate overly permissive policies.
Conclusion: Strengthening AWS Security Through Logging and Monitoring
This blog post has demonstrated that AWS logging and monitoring provide centralized visibility and unified log management for security teams and administrators. This enables security personnel to perform proactive monitoring of the AWS environment, along with establishing automated response workflows. Furthermore, these processes, practices, and workflows provide integrated threat detection, investigation, and remediation. Ultimately, they facilitate effective governance and compliance, as well as lifecycle optimization for sustainability.
Further Reading on AWS Logging and Monitoring
AWS Security
by Dylan Shields
Mastering AWS Security: Strengthen your cloud environment using AWS security features coupled with proven strategies
by Laurent Mathieu
AWS Security Cookbook: Practical solutions for securing AWS cloud infrastructure with essential services and best practices
by Heartin Kanikathottu
Security Best Practices on AWS: Learn to secure your data, servers, and applications with AWS
by Albert Anthony
AWS Certified Security Study Guide: Specialty (SCS‑C01)
by Marcello Zillo Neto
Affiliate Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. This means that if you click on one of the Amazon links and make a purchase, I may receive a small commission at no additional cost to you. This helps support the site and allows me to continue creating valuable content.


