Introduction to Automated Incident Response in AWS
Automated Incident Response in AWS is a core best practice as introduced in AWS Incident Response Best Practices.
Organizations need to maintain an incident response playbook given the escalating cyberthreat landscape. As cloud computing has become an integral part of modern life, cloud-based attacks have increased exponentially, including ransomware, credential theft, and insider threats. These attacks have increased in frequency and in sophistication, where any cloud-based system must have security as part of its DNA. Additionally, traditional manual techniques are obsolete because they are too slow to respond adequately to fast-moving threats.
Not only are threats fast-moving and sophisticated, but AWS environments have increased in scale and complexity, overwhelming manual processes. Many AWS services generate high event volumes, including CloudTrail, GuardDuty automated response, and Security Hub. This clearly necessitates the need for automated incident response. Specifically, human teams are unable to triage incidents fast enough at AWS scale, enabling attackers to find vulnerabilities in any defense quickly.
Furthermore, there are business and regulatory pressures where organizations can best comply by adopting automated incident response in AWS. Incidents inevitably cause downtime that results in financial loss and reputational damage for organizations. Additionally, regulatory authorities subject organizations to compliance frameworks, including PCI DSS, HIPAA, and SOC 2. Therefore, they legally enforce a rapid response to incidents. To meet these strict reporting timelines, organizations must adopt automated incident responses.
The benefits of AWS automated incident response include speed and consistency, satisfying regulatory requirements. Additionally, security engineers can build automated incident response systems that integrate natively with AWS services, including Lambda, EventBridge, and Systems Manager. Furthermore, this frees security engineers to focus on strategy instead of fighting fires.
What is Automated Incident Response?
Definition and Core Concept
Automated incident response utilizes technology and a set of predefined rules to detect and remediate security incidents automatically. Therefore, it minimizes human intervention that is often overloaded and error-prone. These technologies and predefined rules are typically implemented through scripts and workflows; they are also implemented with other tools like GuardDuty automated response. Nonetheless, it is not AWS-specific but applies broadly across all security operations that are cyberattack targets.
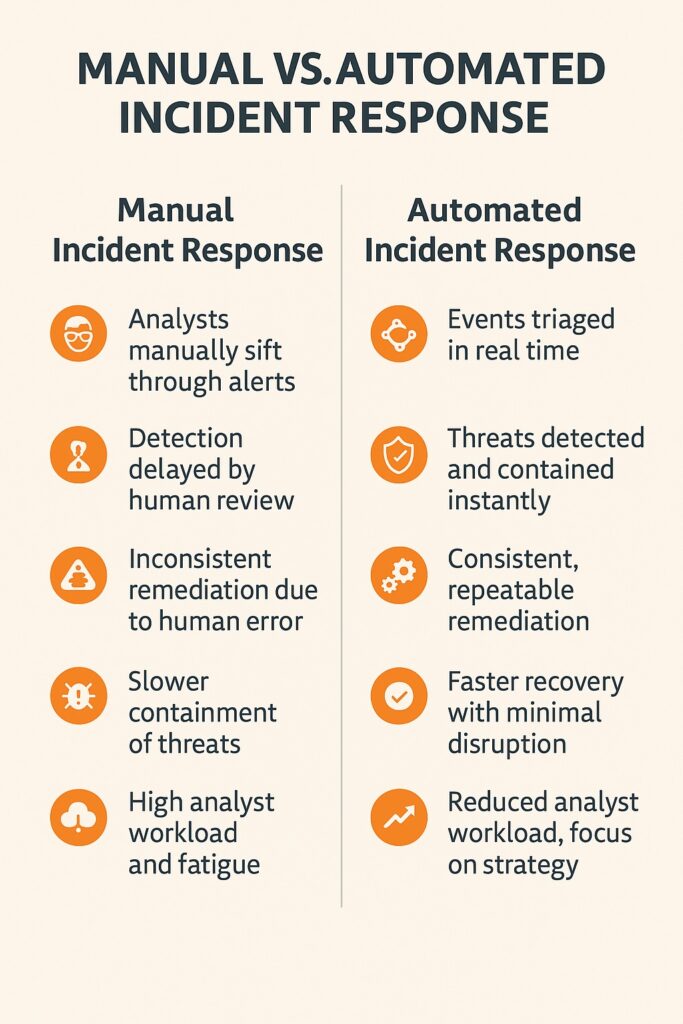
Manual vs. Automated Incident Response Workflows
Alerts, logs, or monitoring tools contain potential security events. Incident response is the process of identifying these events as incidents and remediating them accordingly. Manual workflows require security analysts to manually sift through alerts one by one, which delays detection and response. Additionally, manual investigation and playbook execution involve the risk of human error and inconsistent remediation. However, automated workflows utilize SOAR platforms, SIEM rules, or orchestration scripts that detect threats and trigger responses in real-time. Subsequently, they enable instant, repeatable, and scalable responses, reducing risk exposure and analyst workload.
Benefits of Automation
Expanding on the benefits of automated incident response in AWS, it shortens the detection-to-response cycle from hours to minutes. Thereby reducing the window of potential damage. Security teams still have a manual role to play; however, they no longer have thousands of events every day overwhelming them. Additionally, it is crucial to apply security policies consistently across incidents, which automated workflows ensure. Furthermore, automation reduces reliance on manual intervention, thereby minimizing the likelihood of human error during critical response actions.
Industry Examples
Some examples in industry can further illustrate automated incident response and show it in practice. In the financial sector, automated workflows can lock accounts immediately whenever they detect suspicious transactions. Furthermore, banks and trading platforms use automation to flag anomalies in real time to prevent fraud at scale. Also, in the healthcare sector, automated response tools can isolate compromised endpoints to ensure the protection of sensitive patient data. Finally, cloud and SaaS providers can integrate monitoring with automated response, such as blocking malicious IP addresses before they spread.
Why Automating Incident Response Matters in AWS
There are several key reasons why it is necessary to automate incident response within AWS.
Scale of Modern AWS Environments
AWS cloud computing operates at a large scale for many large and medium-sized organizations. These environments encompass hundreds of accounts, services, and regions, creating massive operational complexity. Also, the monitoring services, like CloudTrail, GuardDuty automated response, and SecurityHub, generate thousands of events daily, quickly overwhelming manual analysis. Additionally, all the microservices and distributed workloads increase the attack surface exponentially, making real-time visibility essential. Hence, automation enables teams to triage and respond at cloud scale, which human analysts alone cannot do.
Speed of Threat Containment
Automated incident response in AWS is vital since cyberattacks in AWS environments can spread within minutes, leaving little time for manual intervention. However, implementing automated workflows can instantly isolate compromised EC2 instances or revoke IAM credentials. Hence, rapid containment will prevent attackers from escalating privileges or moving laterally between accounts. Automation ensures faster response times, minimizing both data loss and business disruption during an incident.
Compliance and Governance Alignment
Many organizations leveraging AWS are increasingly subject to regulatory compliance around security, necessitating automated incident response. In fact, regulations like PCI DSS, HIPAA, and SOC 2 require that organizations respond to security incidents within strict timelines. Another benefit is that automated responses ensure consistent compliance with governance policies across all AWS accounts and regions. Additionally, automation ensures that audit trails are complete by reducing manual lag and that compliance reporting is accurate. Furthermore, automation supports continuous adherence to the AWS Well-Architected Security Pillar by embedding compliance into daily operations.
Financial and Operational Impact
Automated incident response has a direct impact on costs and operations for organizations utilizing the AWS cloud. They mitigate delayed reactions to incidents that potentially result in costly downtime, directly impacting revenue. Automation also reduces recovery time objectives, thereby enabling organizations to restore services more quickly. Additionally, automation minimizes human error and therefore prevents operational disruptions that can ripple across business units. Hence, faster containment and recovery will preserve customer trust, protecting long-term business value.
Building a Resilient Security Culture
Embedding automated incident response directly into AWS operations will reinforce a proactive security mindset. Subsequently, teams will gain confidence that robust incident response systems will address critical threats instantly and reduce reliance on ad-hoc firefighting. Also, making automated responses consistent will free security engineers to focus on strategic improvements rather than on repetitive manual tasks. Furthermore, embedding automation into workflows will shift from a reactive security mindset to a proactive one with a culture of continuous resilience.
AWS Services for Automated Incident Response
AWS provides several services that enable automated incident response within its own infrastructure.
GuardDuty Automated Incident Response
Overview
Amazon GuardDuty is a continuous threat detection service monitoring AWS accounts, workloads, and data, enabling automated incident response for malicious activity. Specifically, it utilizes machine learning, anomaly detection, and threat intelligence feeds for identifying suspicious behavior. Examples of its findings include compromised IAM credentials, unusual API calls, and connections to known malicious IPs.
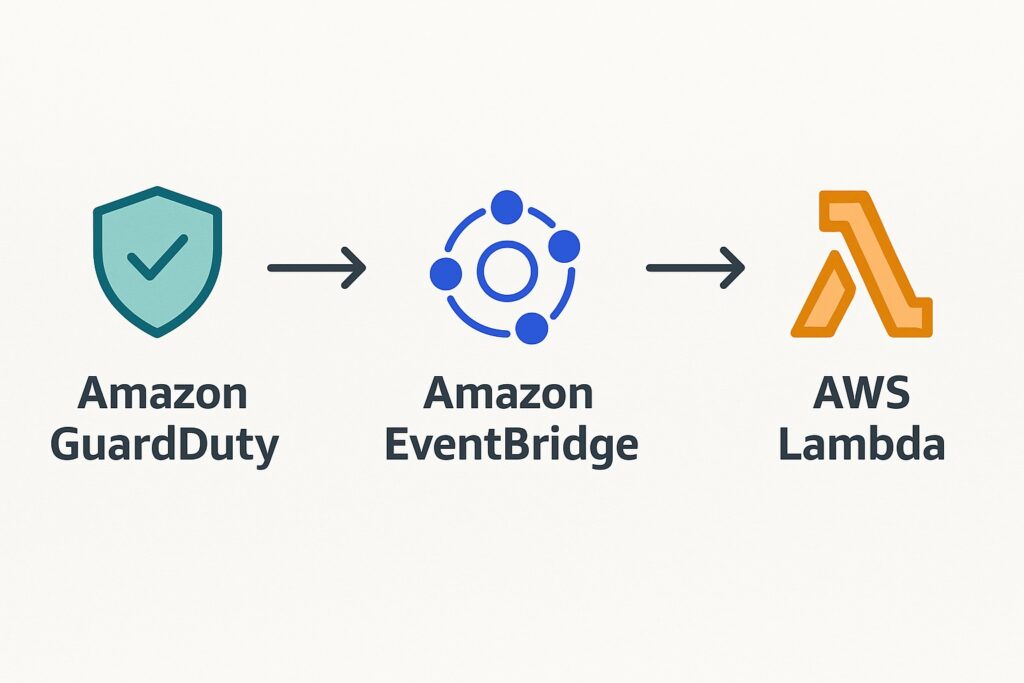
Event Integration
To enable AWS automated incident response, GuardDuty automatically publishes its findings as events to Amazon EventBridge in near real time. Security engineers configure EventBridge rules to match specific findings and route them to appropriate targets. Subsequently, these events are configured to trigger AWS Lambda functions or Step Functions workflows that execute predefined actions, responding to these events.
GuardDuty Automated Incident Response Actions for AWS
There are several common incident response actions that security engineers can automate using GuardDuty coupled with AWS Lambda or Step Functions. Engineers can configure GuardDuty finds to trigger Lambda functions that quarantine compromised EC2 instances by adjusting their security groups. Another action is to revoke or automatically rotate any IAM access keys that GuardDuty suspects are compromised. Also, automated incident response can configure AWS Network Firewall or AWS WAF to block malicious IP addresses at the VPC level. Similarly, Step Functions can orchestrate multi-step responses, such as isolating resources and notifying security teams simultaneously.
Compliance and Governance Alignment
Automated responses to GuardDuty findings ensure that security policies are enforced consistently across all AWS accounts and regions. Additionally, each response action generates useful logs that provide a reliable audit trail for compliance reporting. Therefore, automation assists organizations with meeting regulatory requirements by reducing response times to security incidents.
Best Practices for AWS GuardDuty Automated Incident Response
There are several best practices, including testing and validating automated response playbooks in a staging environment before production deployment. Additionally, security engineers should carefully design containment actions to avoid disrupting critical business workloads. Furthermore, organizations should continuously review and update automation rules as threat patterns and AWS services evolve. Finally, engineers should integrate GuardDuty with AWS Security Hub to centralize visibility and aggregate findings across multiple accounts.
AWS Security Hub Automated Incident Response
Overview
Several AWS services monitor the AWS ecosystem for malicious activity; however, organizations want to centralize these findings for coordinated automated incident response. Therefore, AWS Security Hub is a centralized service that aggregates findings from GuardDuty, Inspector, Macie, and third-party tools. It provides a unified dashboard for security engineers that allows monitoring of the overall security posture and compliance status across AWS accounts. Furthermore, it normalizes findings into the AWS Security Finding Format (ASFF) to ensure consistency and integration.

Event Integration
Security engineers set up automated routing of Security Hub findings to Amazon EventBridge. This is similar for GuardDuty incident response. EventBridge enables event-driven processing for these findings. Security Engineers also define EventBridge rules to detect specific compliance or security issues. Subsequently, these rules trigger automated workflows either using Lambda functions, Step Functions, or third-party integrations.
AWS Automated Incident Response Actions
There are several common actions associated with Security Hub findings that engineers configure handlers, like Lambda, to perform. Findings that are low severity are typically auto-closed to reduce noise and focus attention on critical issues. In the case of misconfigured resources, such as publicly exposed S3 buckets, response handlers can remediate them automatically. However, automated handling should also alert security personnel on high-priority incidents through Amazon SNS, email, or Slack integrations. Finally, engineers should launch Systems Manager Automation runbooks to enforce standardized remediation steps.
Compliance and Governance Alignment
Security Hub’s value also includes mapping findings against compliance standards such as CIS Benchmarks, PCI DSS, and HIPAA. This goes along with the fact that automated workflows ensure the remediation of non-compliant resources consistently across accounts. Additionally, AWS Security Hub supports automated incident response by automatically generating compliance reports and audit-ready evidence to support regulatory requirements.
Best Practices for AWS Security Hub Automated Incident Response
Following best practices is vital, and security engineers should continuously tune automation rules to minimize false positives and improve accuracy. This topic is discussed in detail in “Tame Imbalanced Data with Smart Classification Tips.” While automated incident response is the foundation, there is no replacement for manually reviewing high-impact findings to avoid unintended disruptions. Additionally, support Security Hub with multi-account aggregation in AWS organizations for consistent policy enforcement. Finally, combine Security Hub automation with GuardDuty automated response to create a layered defense approach, or defense in depth.
Incident response automation with AWS Lambda
Overview
AWS Lambda functions perform the automated incident response actions, where AWS GuardDuty and Security Hub actively screen for malicious activities. It is a serverless compute service that runs code without the need to manage servers. It supports incident response by executing functions automatically in response to triggers from other AWS services or external events. Therefore, it is well-suited for lightweight, event-driven security automation tasks.
Event Integration
AWS Lambda can perform the actual incident response automatically by integrating directly with services such as EventBridge, CloudWatch, and GuardDuty. Specifically, engineers can configure triggers to launch Lambda functions automatically whenever specific incident patterns occur. Subsequently, this integration enables near real-time execution of custom remediation logic tailored to organizational needs.
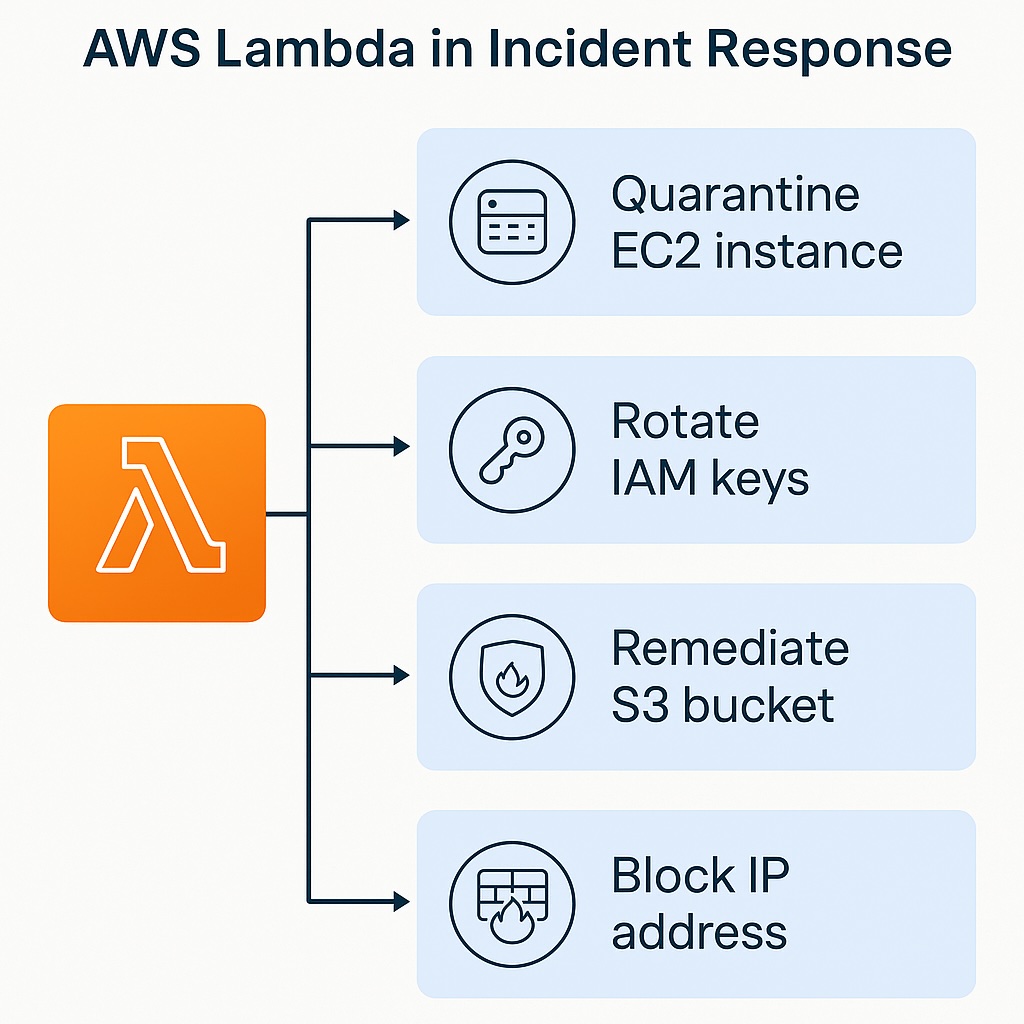
AWS Automated Incident Response Actions
There are several automated incident response actions where Lambda functions are ideal. First, quarantine compromised EC2 instances by modifying their security group rules. Second, Lambda functions can automatically rotate IAM access keys or disable accounts flagged for suspicious activity. Third, they can remediate misconfigured S3 buckets by enabling encryption or restricting public access. Lastly, they can send enriched incident details to security teams through SNS, Slack, or ticketing systems.
Compliance and Governance Alignment
Lambda functions’ other advantage is that they allow security engineers to enforce security policies programmatically across all AWS accounts and resources. They also support traceability for audits and compliance verification by generating logs for each execution. Furthermore, automated enforcement ensures consistent governance and reduces the risk of manual oversight.
Best Practices for AWS Automated Incident Response with Lambda Functions
There are several guidelines that engineers should follow to use Lambda functions effectively. Primarily, they should ensure that Lambda functions are always lightweight and modular to avoid execution timeouts and cost inefficiencies. Additionally, engineers should apply the principle of least privilege when assigning IAM roles to Lambda functions. As part of CI/CD practices, engineers should test functions in non-production (or staging) environments before deploying them to prevent unintended impacts. Finally, as part of good software lifecycle management, engineers should use versioning and CloudWatch monitoring to track performance and troubleshoot issues.
Building Automated Incident Response Playbooks in AWS
Automated incident response here is that engineers can implement playbooks programmatically, ensuring consistency and the ability to troubleshoot any issues. However, we must note that there must be a manual oversight component for a complete security posture.
Overview of Playbooks
Automated incident response playbooks are predefined workflows that standardize how security incidents are handled. Specifically, they provide step-by-step actions that are automatically executed by AWS services like Lambda functions when specific conditions are met. Therefore, they reduce the time needed to contain and remediate threats by eliminating manual delays and decision-making processes. Furthermore, they minimize human error by enforcing consistent response actions across incidents. Engineers can utilize AWS services, such as Systems Manager, Lambda, and EventBridge, as building blocks to implement automated playbooks.
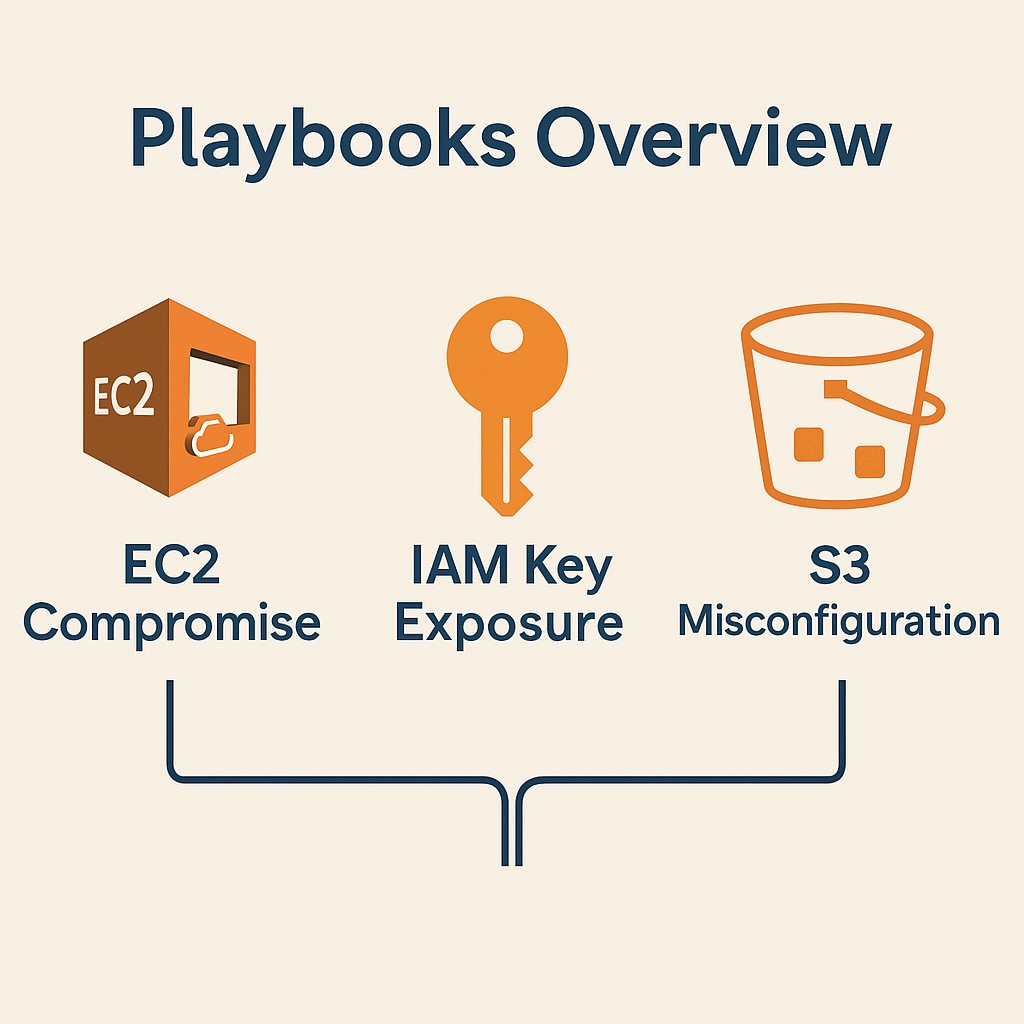
Common Playbook Use Cases
There are several common use cases involving security incident response that are invariably included in any AWS security incident response playbook. A playbook for comprised EC2 instances typically isolates the affected instance, snapshots it for forensics, and blocks its internet access. Playbooks for IAM key exposure usually disable the compromised key, rotate credentials, and notify the security team. Regarding S3 misconfigurations, playbooks should restrict public access, enable encryption, and log access attempts automatically. In the case of malicious IP detection, playbooks should block the IP using Network Firewall or WAF and update deny lists.
AWS Services Supporting Playbooks
Several AWS services support playbooks, which were covered early and are reiterated here. AWS Systems Manager Automation runbooks codify predefined remediation steps for common incidents mentioned previously. GuardDuty and Security Hub are the primary sources of findings of malicious activities responsible for initiating automated playbooks for response to incidents. Next, Amazon EventBridge connects these sources to playbooks by triggering them whenever specific security conditions are met based on any findings. Finally, AWS Lambda performs custom remediation logic when triggered by EventBridge to extend playbooks with fine-grained automation.
Compliance and Audit Support
Automating playbooks will ensure that incidents are handled consistently across accounts and comply with governance requirements. Additionally, each playbook execution generates logs and outputs that create a reliable audit trail for compliance reporting. Also, automated playbooks allow organizations to demonstrate that they are adhering to frameworks like PCI DSS, HIPAA, and the AWS Well-Architecture Security Pillar.
Best Practice Considerations
Implementing automated playbooks has an associated set of best practices to ensure compliance with security guidelines. Engineers should apply CI/CD practices by testing automated playbooks thoroughly in staging environments before deploying them into production. Similar to good software development practices, readability is paramount for playbook documentation, allowing analysts to understand their purpose, scope, and limitations. Human overview is still needed for destructive or high-risk actions to prevent unintended disruptions. Finally, applying CI/CD practices ensures continuous updating of playbooks as threat models evolve and AWS services add new features.
Challenges and Considerations for AWS Automated Incident Response
When implementing automated playbooks, several key considerations can hinder an effective security posture and increase the risk of severe consequences.
False Positives and Alert Fatigue
Frequent false alarms are severe for several reasons, as they potentially disrupt workloads and erode trust in automation. Furthermore, security teams develop alert fatigue and become desensitised to alerts. Like the story of the boy who cried wolf, this can reduce their effectiveness in real incidents. A high number of false alarms results from overly sensitive detection rules that trigger automated responses for events that are not actual security incidents.

Risk of Over-Automation
Whereas manual-based response is invariably delayed and error-prone, fully automated responses can cause havoc without any manual oversight. They can shut down instances automatically and disrupt business services. Also, many incidents are unsuitable for automated handling and require some human judgment and context. Furthermore, over-reliance on automation can create blind spots where nuanced threats go undetected.
Complexity of Multi-Account Environments
Whereas consistency across the organization is desired, organizations running hundreds of AWS accounts make consistent automation rules difficult to enforce. Automation also introduces overhead when implementing incident response orchestration across multiple regions. These overheads include latency and management challenges. Furthermore, ensuring centralized visibility and control in multi-account setups requires careful design, utilizing AWS Organizations and Security Hub.
Cost Implications
Implementing AWS services like Lambda, Step Functions, and Event Bridge to support automated workflows will incur costs that organizations need to manage. Furthermore, storing detailed logs for compliance in S3 and CloudWatch can also incur costs, especially CloudWatch. Therefore, organizations need to weigh up the cost of automation with the operational benefits and arrive at an economically and efficacious solution.
Skill and Maintenance Requirements
Whereas automation replaces many manual processes, it still demands human expertise in its design, implementation, and maintenance. In fact, greater expertise is needed, especially in AWS services and security practices. Because the threat landscape is continually evolving, engineers need to update playbooks and workflows continuously. Therefore, without proper maintenance, outdated automation will certainly increase security risks through gaps that start appearing.
Future Trends: SOAR in AWS and Beyond
The threat landscape is evolving, and so are the tools needed to counteract these threats.
Rise of Cloud-Native SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response)
The AWS services that support automated incident response are increasingly providing SOAR-like (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) capabilities natively. They enable organizations to orchestrate detection, triage, and response entirely within the AWS ecosystem. Subsequently, this development reduces reliance on external SOAR platforms by consolidating security automation into AWS-native workflows.
Integration with AI/ML for Smarter Automated Incident Response
AI and ML are now a significant component of the security arsenal, and no security posture is complete without them. Machine learning models can reduce false positives by analyzing patterns and distinguishing normal behavior from real threats. Meanwhile, AI-driven anomaly detection enables more rapid identification of previously unseen attack vectors. Additionally, predictive analytics can anticipate potential incidents and trigger proactive response measures.
Cross-Platform and Hybrid Cloud Incident Response Automation
Many organizations do not operate solely in AWS, but across multiple cloud environments and their on-premises networks. Therefore, they need to set up unified playbooks for incident response. However, vendors and AWS partners are building integrations that extend automation beyond a single cloud provider. Subsequently, they need hybrid cloud automation that ensures consistent security operations across on-premises systems and multiple cloud environments.
Greater Emphasis on Compliance Automation
Along with incident response automation, there is a need to automate compliance. This is typically achieved by directly integrating automated incident response into compliance dashboards for real-time visibility. Another benefit is that continuous evidence collection will simplify audits for frameworks like PCI DSS, HIPAA, and SOC 2. Therefore, automation ensures that compliance reporting is accurate, consistent, and less dependent on manual processes.
Shift Toward Autonomous Security Operations
Further ahead is the advent of autonomous security operations with security automation progressing from being reactive to a self-healing infrastructure. Therefore, future AWS environments may detect, contain, and remediate incidents with minimal or no human intervention. This evolution will transform security operations into proactive, autonomous systems continuously adapting to new threats.
Conclusion
Given the scale and speed of today’s cloud environments like AWS, it is essential to automate incident response. This is because manual response methods are unable to keep pace with the volume and complexity of modern cyberattacks.
The benefits associated with automated incident response are quicker containment, reduced downtime, consistent compliance, and minimized human errors. Also, security teams can focus more of their time on strategy instead of firefighting.
Security engineers can create seamless incident response automation by using AWS services, including GuardDuty, Security Hub, Lambda, and Systems Manager. They can also codify playbooks that orchestrate these services into repeatable, standardized workflows.
However, engineers need to factor in issues like over-automation, false positives, and balancing cost. Also, AWS skill development and ongoing maintenance are critical for success.
This field is also continually evolving with AWS services progressing toward SOAR-like native AWS capabilities. Also, AI-driven detection and autonomous operations are developments that will influence future operations.
There are two related articles on this subject. The first is AWS Incident Response Best Practices, while the other is Mastering AWS CloudTrail.
Start building automated playbooks with GuardDuty, Security Hub, and Lambda to strengthen resilience.
Further Reading
AWS Certified Security – Specialty Exam Guide by Stuart Scott
Covers exam domains, including incident response, logging, monitoring, and compliance.
Infrastructure as Code, 2nd Edition by Kief Morris
Not AWS-specific, but essential for codifying incident response playbooks and automating security at scale.
AWS Security Cookbook by Heartin Kanikathottu
Practical, recipe-based approach to securing AWS workloads and automating responses.
Cloud Security Handbook by Eyal Estrin
Comprehensive resource on securing cloud workloads with AWS focus, governance, and compliance.
AWS Cookbook by John Culkin & Mike Zazon (O’Reilly)
Hands-on solutions for AWS automation, including Lambda, EventBridge, and security workflows.
Practical Cloud Security: A Guide for Secure Design and Deployment by Chris Dotson
Design principles and practical strategies for incident response in AWS and hybrid environments.
Affiliate Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. This means that if you click on one of the Amazon links and make a purchase, I may receive a small commission at no additional cost to you. This helps support the site and allows me to continue creating valuable content.


